스프링 부트
1. 스프링 부트 소개
스프링 부트의 획기적인 네 가지 기능
스프링 부트 스타터 - 프로젝트의 메이븐이나 그래들 빌드에 추가 가능한, 일반적인 그룹화된 의존을 단일 의존으로 모음
자동 설정 - 합리적으로 어플리케이션이 필요한 빈을 추측하고, 자동으로 설정하기 위한, 조건부 설정 기능 제공
커맨드라인 인터페이스 - 스프링 어플리케이션 개발을 더 간단하게 해주기 위해, 자동 설정에서 그루비 프로그래밍 언어의 장점 활용
액추에이터 - 스프링 부트 어플리케이션에 특정 관리 기능 추가
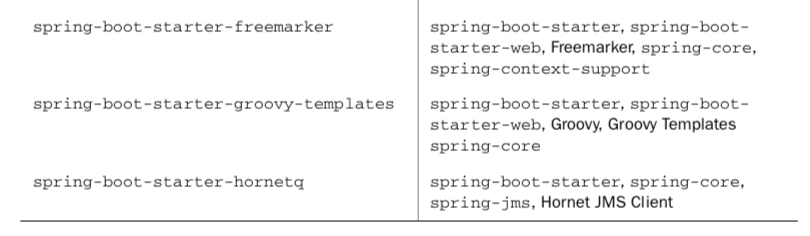
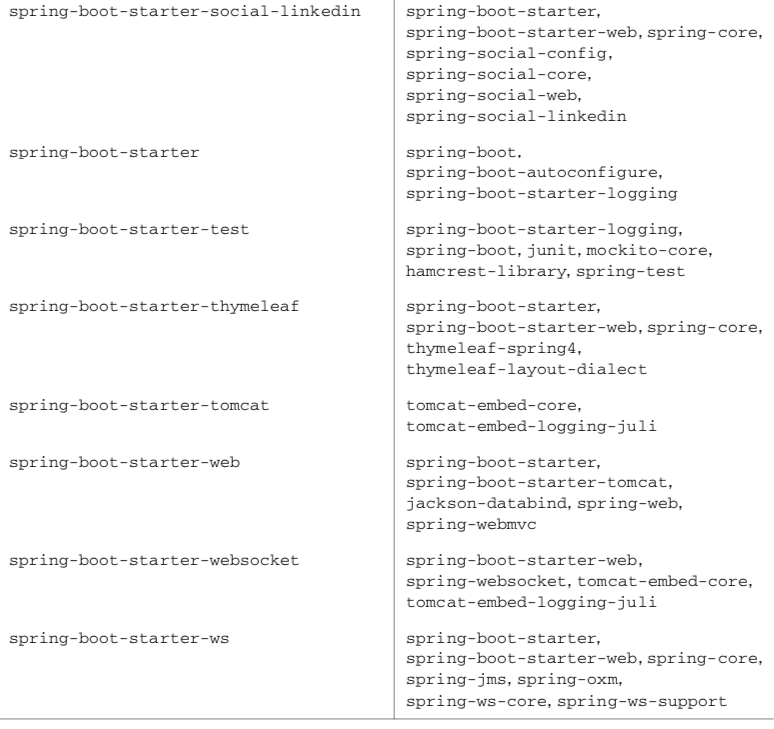
1.1 스타터 의존 추가
* 그래들과, 메이븐으로 간결하게 의존성을 표현할 수 있다.
dependencies {
compile("org.springframework:spring-web:4.0.6.RELEASE")
compile("org.springframework:spring-webmvc:4.0.6.RELEASE")
compile("com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-databind:2.2.2")
compile("org.springframework:spring-jdbc:4.0.6.RELEASE")
compile("org.springframework:spring-tx:4.0.6.RELEASE")
compile("com.h2database:h2:1.3.174")
compile("org.thymeleaf:thymeleaf-spring4:2.1.2.RELEASE")
}* spring-web, spring-webmvc, jackson 라이브러리, spring-jdbc, spring-tx, h2database, thymeleaf 를 의존성 추가
==> 이를 스타터로도 묶을 수 있다
dependencies {
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:
1.1.4.RELEASE")
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jdbc:
1.1.4.RELEASE")
compile("com.h2database:h2:1.3.174")
compile("org.thymeleaf:thymeleaf-spring4:2.1.2.RELEASE")
}* 메이븐 생략


1.2 자동 설정
스트링 부트 스타터는 의존성 목록의 크기를 줄여주고, 자동 설정은 설정의 양을 줄인다
* 예를 들어, 6장의 Thymeleaf를 사용하기 위해, ThymeleafViewResolver, SpringTemplateEngine, TemplateResolver가 필요했다면, 스프링 부트의 자동설정에서는, 단순히 Thymeleaf를 프로젝트 클래스패스에 넣어주기만 하면 된다
=> 클래스패스에서 발견할 때, 위의 세개의 빈을 자동으로 설정
* 스프링 MVC를 사용하기 위해, 웹 스타터를 추가하면 되며 마찬가지로 자동으로 필요한 빈을 생성해준다 => 남은 것은 요청을 처리하는 컨트롤러 클래스 작성 뿐
1.3 스프링 부트 CLI
스프링 부트 CLI는 그루비를 사용한다. 이 기능으로 개발 프로세스가 간결해 진다
@RestController
class Hi {
@RequestMapping("/")
String hi() {
"Hi!"
}
}* 해당 그루비 스크립트를, CLI가 깔려있다면 [$ spring run.Hi.groovy ] 라는 명령어로, 실행할 수 있다.
1.4 액추에이터
간편하고 유용한 기능들을 제공한다
앤드포인트 관리
실용적인 오류 처리, /error 엔드포인트 기본 세팅
어플리케이션의 정보를 전달하는 /info 엔드포인트
스프링 시큐리티가 동작할 때 검증 이벤트 프레임워크
2. 스프링 부트로 애플리케이션 만들기
* 간단한 연락처 어플리케이션 제작
* build.gradle
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenLocal()
}
dependencies {
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:
1.1.4.RELEASE")
}
}
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'spring-boot'
jar { // JAR파일로 빌드
baseName = 'contacts'
version = '0.1.0'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
// 의존성은 이 곳에 추가
}
task wrapper(type: Wrapper) {
gradleVersion = '1.8'
}* 같은 동작을 하는 pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.habuma</groupId>
<artifactId>contacts</artifactId>
<version>0.1.0</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.1.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
### 이곳에 의존성 추가
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>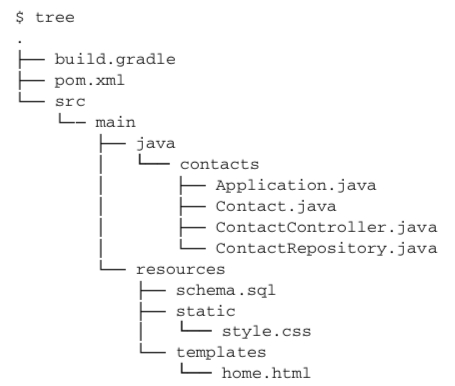
2.1 요청 처리하기
* 스프링 MVC로 웹 레이어를 개발할 것이므로, 의존성에 웹 스타터를 추가한다
// 그래들
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web")# 메이븐
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>* 어플리케이션의 컨트롤러 작성을 위한 모든 준비가 끝
* HTTP GET 요청에 대한, 연락처 폼을 보여주고 POST 요청을 처리하여 폼 제출을 하는 컨트롤러
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/")
public class ContactController {
private ContactRepository contactRepo;
@Autowired
public ContactController(ContactRepository contactRepo) { // 레포지토리 주입
this.contactRepo = contactRepo;
}
@RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.GET) // GET 처리
public String home(Map<String,Object> model) {
List<Contact> contacts = contactRepo.findAll();
model.put("contacts", contacts);
return "home";
}
@RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.POST) // POST 처리
public String submit(Contact contact) {
contactRepo.save(contact);
return "redirect:/";
}
}
* Contact 객체
public class Contact {
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String phoneNumber;
private String emailAddress;
// 설정자, 접근자 생략
}=> 남은 것은 home 뷰를 정의하는 것
2.2 뷰 만들기
* Thymeleaf를 사용하여, 편리한 HTML 템플릿을 작성한다
// 그래들
compile("org.thymeleaf:thymeleaf-spring4")# 메이븐
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring4</artifactId>
</dependency>* 스프링 부트는, 자동적으로 뷰리졸버, 템플릿리졸버, 템플릿 엔진을 빈으로 설정한다. 따라서 명시적으로 스프링 설정을 해줄 필요가 없음
### home.html 파일
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Spring Boot Contacts</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" th:href="@{/style.css}" />
</head>
<body>
<h2>Spring Boot Contacts</h2>
<form method="POST">
<label for="firstName">First Name:</label>
<input type="text" name="firstName"></input><br/>
<label for="lastName">Last Name:</label>
<input type="text" name="lastName"></input><br/>
<label for="phoneNumber">Phone #:</label>
<input type="text" name="phoneNumber"></input><br/>
<label for="emailAddress">Email:</label>
<input type="text" name="emailAddress"></input><br/>
<input type="submit"></input>
</form>
<ul th:each="contact : ${contacts}">
<li>
<span th:text="${contact.firstName}">First</span>
<span th:text="${contact.lastName}">Last</span> :
<span th:text="${contact.phoneNumber}">phoneNumber</span>,
<span th:text="${contact.emailAddress}">emailAddress</span>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>=> 간단한 연락처 생성 및 목록을 보여주는, home.html
=> Thymeleaf는 클래스패스의 루트인 templates 디렉터리에서 검색하므로, 반드시 src/main/resources/templates 하위에 있어야함
2.3 정적 아티팩트 추가하기
* 스프링 부트의 웹 자동 설정이 스프링 MVC를 위한 빈을 설정할 때, 리소스위치로 /**을 매핑하는 리소스핸들러를 포함
/META-INF/reosources/
/resources/
/static/
/public/
해당 하위 디렉토리에, style.css를 추가하면, Thymeleaf의 템플릿 기준에 만족한다
## style.css
body {
background-color: #eeeeee;
font-family: sans-serif;
}
label {
display: inline-block;
width: 120px;
text-align: right;
}2.4 데이터 보존하기
스프링 부트에서 데이터베이스를 작업하기 위해서는, jdbc 스타터가 필요, H2를 사용하기 위해서는 h2 의존성 추가가 필요
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jdbc")
compile("com.h2database:h2")<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
</dependency>* 마찬가지로, 매우 간결하게 사용할 수 있다 - 템플릿 주입
@Repository
public class ContactRepository {
private JdbcTemplate jdbc;
@Autowired
public ContactRepository(JdbcTemplate jdbc) {
this.jdbc = jdbc;
}
public List<Contact> findAll() {
return jdbc.query(
"select id, firstName, lastName, phoneNumber, emailAddress " +
"from contacts order by lastName",
new RowMapper<Contact>() {
public Contact mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Contact contact = new Contact();
contact.setId(rs.getLong(1));
contact.setFirstName(rs.getString(2));
contact.setLastName(rs.getString(3));
contact.setPhoneNumber(rs.getString(4));
contact.setEmailAddress(rs.getString(5));
return contact;
}
}
);
}
public void save(Contact contact) {
jdbc.update(
"insert into contacts " +
"(firstName, lastName, phoneNumber, emailAddress) " +
"values (?, ?, ?, ?)",
contact.getFirstName(), contact.getLastName(),
contact.getPhoneNumber(), contact.getEmailAddress());
}
}* 스프링 부트에서, JDBC 모듈과 H2를 발견하면, JdbcTemplate 빈과, H2 Datasource 빈을 자동으로 설정
* 당연하게도, 데이터베이스 테이블의 스키마는 직접 정의해주어야 함
create table contacts (
id identity,
firstName varchar(30) not null,
lastName varchar(50) not null,
phoneNumber varchar(13),
emailAddress varchar(30)
);2.5 실행하기
스프링에서 설정해준 , web.xml이나 DispatcherServlet 없이도, 실행 가능
* 어떠한 설정도 필요 없으며, 단지 특별한 클래스 중 하나인, 스프링 부트의 '부트스트랩'만이 필요하다
@ComponentScan
@EnableAutoConfiguration // 자동 설정 활성화
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); // 어플리케이션 실행
}
}* 자동설정 활성화 및 실행 줄 만으로, 실행 가능
* 남은 것은 빌드 뿐 => [$ gradle build] or [$ mvn package] ==> [$ java -jar build/libs/contacts-0.1.0.jar]
=> 이 경우 'jar'로 배포 되지만, war 배포도 충분히 가능하다
apply plugin: 'war'
war { // WAR파일로 빌드
baseName = 'contacts'
version = '0.1.0'
}* 메이븐도 마찬가지로, jar를 단순히 war로만 바꾸어 주면 된다
3. 그루비 사용
=> 그루비는 쓸 때, 찾아보아도 될 것 같아 생략
4. 액추에이터로 애플리케이션 파악하기
액추에이터의 역할은, 스프링 부트 기반의 애플리케이션에 유용한 앤드포인트 관리 기능 추가
GET /autoconfig - 자동설정 적용 시, 스프링 부트에 의한 결정
GET /beans 어플리케이션 실행을 위해 설정되는 빈의 카탈로그
GET /configprops - 현재 값으로 빈을 설정하기 위한 모든 프로퍼티 목록
GET /dump - 각 스레드의 스택 추적을 포함한 스레드 목록
GET /env - 어플리케이션 컨텍스트에서 사용 가능한 모든 환경 변수와 시스템 프로퍼티 값의 목록
GET /env/{name} - 특정 환경 변수나 프로퍼티 값 표시
GET /health - 어플리케이션 상태 표시
GET /info - 어플리 케이션상세 정보 표시
GET /metrics - 특정 앤드포인트에 대한, 요청 개수를 포함한 메트릭 목록
GET /metrics/{name} - 특정 메트릭 키에 대한 메트릭 표시
POST /shutdown - 강제 종료
GET /trace - 최근 요청에 관한 메타데이터 목록
사용하기 위해 의존성 추가
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator")<dependency>
<groupId> org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-actuator</carlsbad>
</dependency>* 액추에이터를 추가하고 나면, 엔드포인트를 통해 많은 정보를 얻을 수 있다.
예시( http://localhost:8080/beans )
$ curl http://localhost:8080/beans
[{
"beans": [
{
"bean": "contactController",
"dependencies": [
"contactRepository"
],
"resource": "null",
"scope": "singleton",
"type": "ContactController"
}, {
}, ... {
"bean": "jdbcTemplate",
"dependencies": [],
"resource": "class path resource [...]",
"scope": "singleton",
"type": "org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"
},
... ]
} ]=> 위에 써진 /beans, /autocofig 등을 한번 사용해보자
Last updated